Glaucoma / Glaucoma: causes and symptoms
Causes of glaucoma
There are certain factors that can increase the risk of developing glaucoma, such as family history (increases the risk of developing glaucoma by up to 10 times), diabetes, smoking myopia and hyperopia, prolonged treatment with corticosteroids, or exposure to the sun. And of course, aging.
Aging is one of the most significant risk factors. With age, the depth and volume of the anterior chamber decreases, increasing the risk of pupillary blockage and thus the prevalence of angle closure glaucoma.
In most cases, glaucoma is associated with high intraocular pressure (ocular hypertension). But it can also occur even when intraocular pressure (IOP) is at normal levels.
Therefore, if glaucoma is not treated or managed in its early stages it can lead to loss of peripheral vision and eventually blindness.
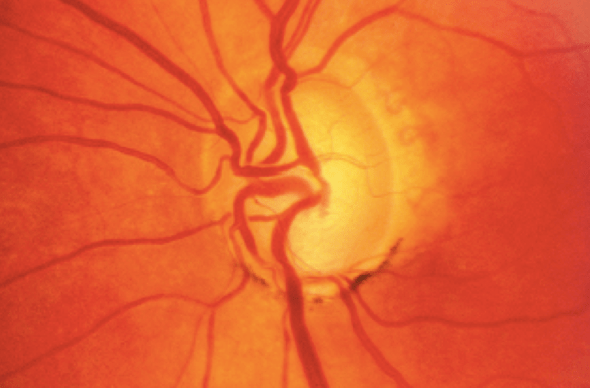
Glaucomatous papilla
Who can develop glaucoma?
We still do not fully understand the causes of this disease, but there are a series of risk factors that we should take into account:
→ Family history of glaucoma.
→ Age: be older than 40 years for African-Americans. Open-angle glaucoma is more likely to affect African-Americans than non-Hispanic Caucasians in the United States and therefore more prevalent in blindness. Other studies explain that open-angle glaucoma affects African-Americans almost equally as it does Latinos and Hispanics.
→ Age: be over 60 years old, especially Mexican-Americans.
→ Having thin cornea.
→ Having abnormal optic nerve anatomy with increased papillary cupping.
→ Having high myopia.
→ Diabetes.
→ Elevated blood pressure.
→ Eye trauma.
Symptoms of glaucoma
Glaucoma is a disease with no symptoms, as in the majority of cases it does not cause pain and may go unnoticed until it causes significant loss of vision.
For this reason, glaucoma can progress silently until it causes irreversible damage to the optic nerve, causing permanent loss of vision at different levels.

Symptoms of closed-angle glaucoma
• In early stages you may notice sudden changes to your vision and experience blurry vision.
• Halos when you stare at a light.
• Other symptoms include severe eye pain, nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms of open-angle glaucoma
• This is the most common form and there are no symptoms in the early stages.
• There is no pain or redness and vision is lost slowly and progressively, beginning with peripheral vision and eventually affecting central vision in much later stages. This means that, in the early stages the patient is often unaware that they even have this disease until it becomes much more advanced, and it is important to remember that lesions caused by glaucoma are irreversible.
• It is very important to identify glaucoma early through regular eye examinations particularly in cases where patients have a family history of glaucoma.
Vision with glaucoma in different phases
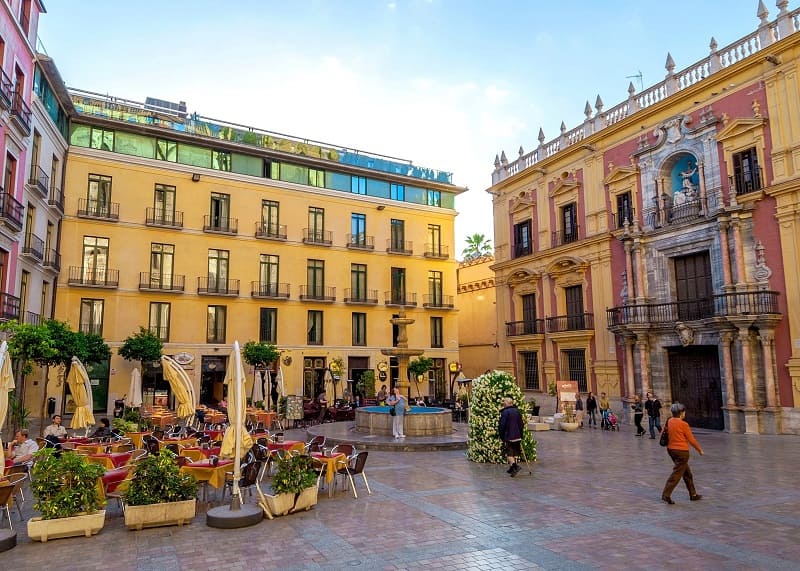

Normal eye
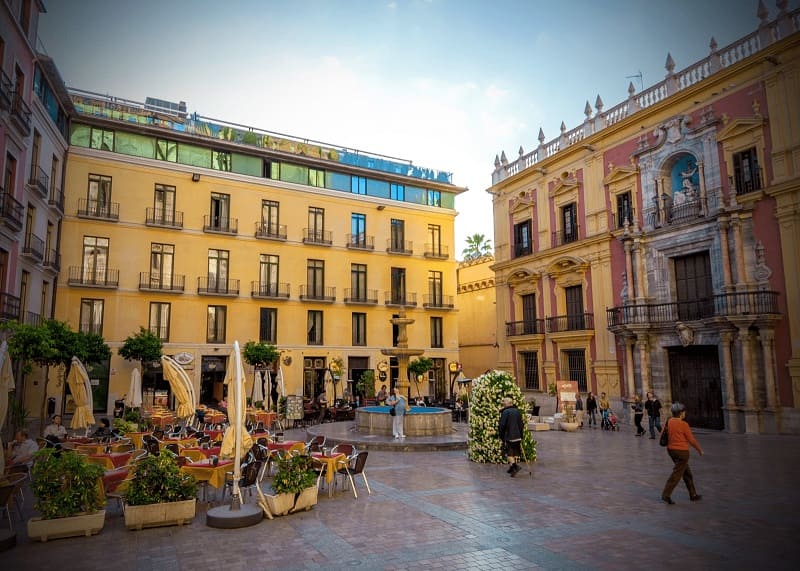

Initial glaucoma
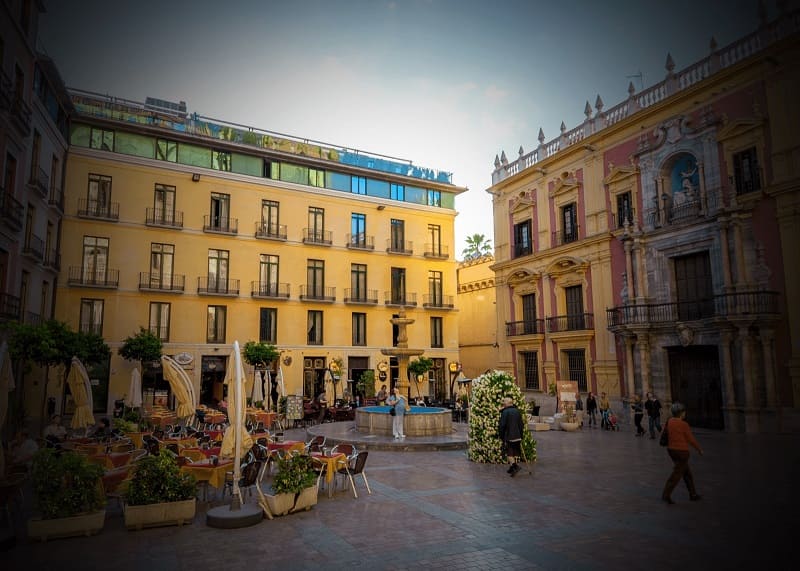

Advanced glaucoma
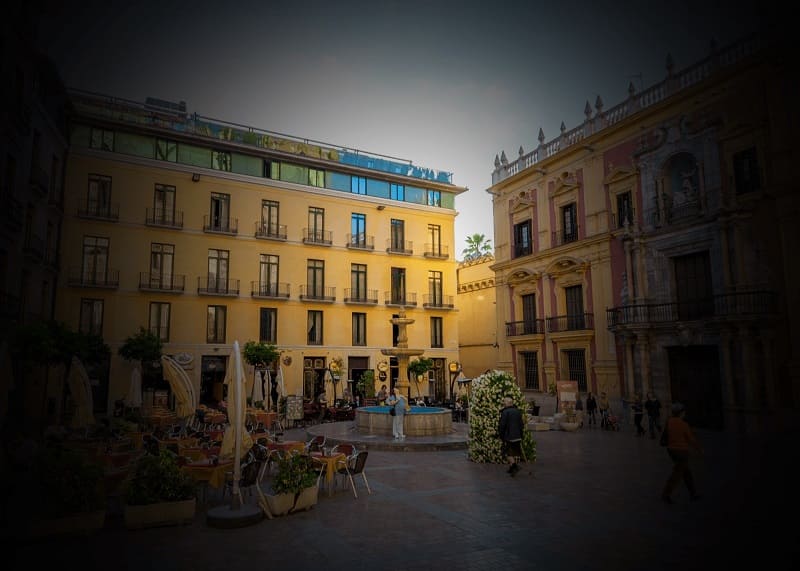

End-stage glaucoma